Automated trading, often referred to as algorithmic trading, is a method of executing trades using pre-defined criteria set by traders. This approach leverages computer algorithms to analyze market conditions and execute trades at speeds and frequencies that are impossible for human traders. The primary advantage of automated trading lies in its ability to remove emotional decision-making from the trading process, allowing for a more disciplined and systematic approach.
Traders can program their strategies based on technical indicators, historical data, and market trends, enabling them to capitalize on opportunities as they arise. The mechanics of automated trading involve the use of sophisticated software that can monitor multiple markets and assets simultaneously. These systems can execute trades based on a variety of factors, including price movements, volume changes, and even news events.
For instance, a trader might set up an algorithm to buy a stock when its price crosses above a certain moving average while simultaneously selling when it dips below another threshold. This level of precision and speed can lead to significant advantages in fast-moving markets, where every second counts.
Key Takeaways
- Automated trading involves using computer programs to execute trading strategies
- Choose an automated trading platform that suits your trading style and needs
- Set up a clear and well-defined trading strategy before implementing automated trading
- Manage risk by setting stop-loss orders and diversifying your portfolio
- Regularly monitor and adjust your automated trades to adapt to market conditions
Choosing the Right Automated Trading Platform
Selecting the appropriate automated trading platform is crucial for the success of any trading strategy. Various platforms offer different features, tools, and levels of customization, making it essential for traders to assess their specific needs before making a choice. Some platforms cater to beginners with user-friendly interfaces and pre-built strategies, while others are designed for experienced traders who require advanced functionalities and extensive customization options.
Popular platforms include MetaTrader 4 and 5, TradeStation, and NinjaTrader, each offering unique capabilities that can enhance the trading experience. When evaluating a trading platform, traders should consider factors such as execution speed, reliability, available markets, and the range of technical indicators offered. Additionally, the platform’s compatibility with various programming languages can be a significant factor for those looking to develop custom algorithms.
For example, MetaTrader allows users to create Expert Advisors using MQL4 or MQL5, enabling traders to tailor their strategies precisely to their requirements. Furthermore, the availability of backtesting features is essential for assessing the viability of a trading strategy before deploying it in live markets.
Setting Up Your Automated Trading Strategy

Establishing a robust automated trading strategy involves several critical steps that require careful consideration and planning. First and foremost, traders must define their objectives clearly. Are they looking for short-term gains through day trading, or are they more interested in long-term investments?
This foundational decision will influence the choice of indicators, timeframes, and risk management techniques employed in the strategy. For instance, a day trader might focus on minute-by-minute price movements and employ scalping techniques, while a swing trader may look at daily or weekly charts to capture larger price swings. Once the objectives are established, traders should conduct thorough research to identify suitable indicators and market conditions that align with their goals.
This may involve analyzing historical data to determine which indicators have performed well under specific circumstances. For example, a trader might find that a combination of the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and moving averages provides reliable signals for entry and exit points in a particular market. After selecting the indicators, traders can begin programming their algorithms to execute trades based on these criteria, ensuring that they incorporate proper risk management measures throughout the process.
Managing Risk in Automated Trading
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| Volatility | The measure of the variation of price of a financial instrument over time. |
| Drawdown | The peak-to-trough decline during a specific period of an investment. |
| Sharpe Ratio | A measure for calculating risk-adjusted return, which is the average return earned in excess of the risk-free rate per unit of volatility or total risk. |
| Maximum Loss | The maximum amount of capital that an investor or trader can lose in a single trade or investment. |
Risk management is an integral component of any successful trading strategy, particularly in automated trading where emotions are removed from the equation. Traders must establish clear parameters for how much capital they are willing to risk on each trade and set stop-loss orders accordingly. A common approach is to risk only a small percentage of the total trading capital on any single trade—typically between 1% to 3%.
This strategy helps protect the overall portfolio from significant losses while allowing for potential gains over time. In addition to setting stop-loss orders, traders should also consider diversifying their automated trading strategies across different assets or markets. By spreading risk across various instruments, traders can mitigate the impact of adverse movements in any single asset.
For instance, an automated trading system that operates in both forex and commodities markets can reduce overall volatility compared to one that focuses solely on equities. Furthermore, regular monitoring of the performance of each strategy is essential to ensure that they continue to align with market conditions and risk tolerance levels.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Automated Trades
Even though automated trading systems operate independently once set up, continuous monitoring is vital to ensure optimal performance. Market conditions can change rapidly due to economic events, geopolitical developments, or shifts in investor sentiment. As such, traders should regularly review their automated strategies to assess their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
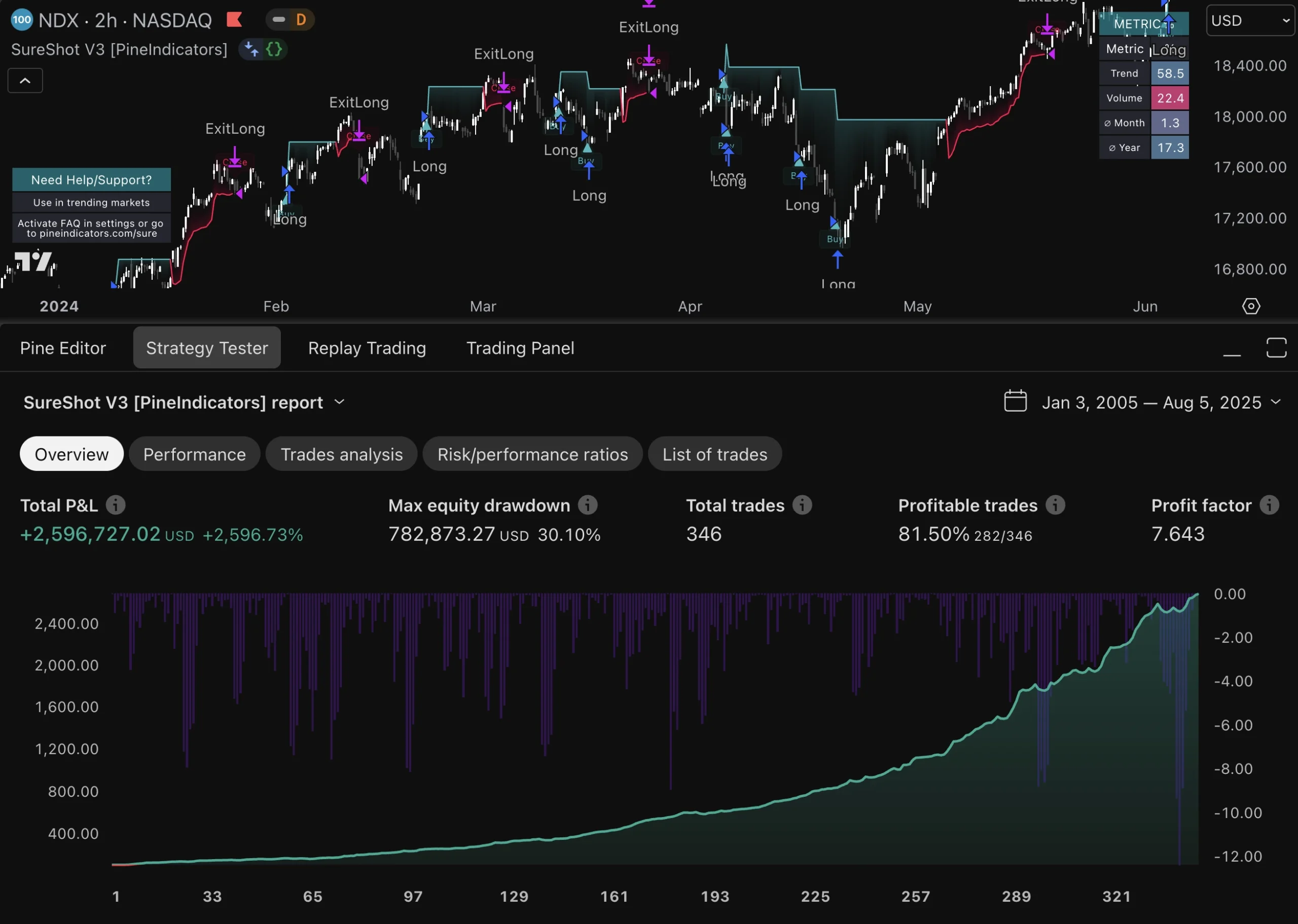
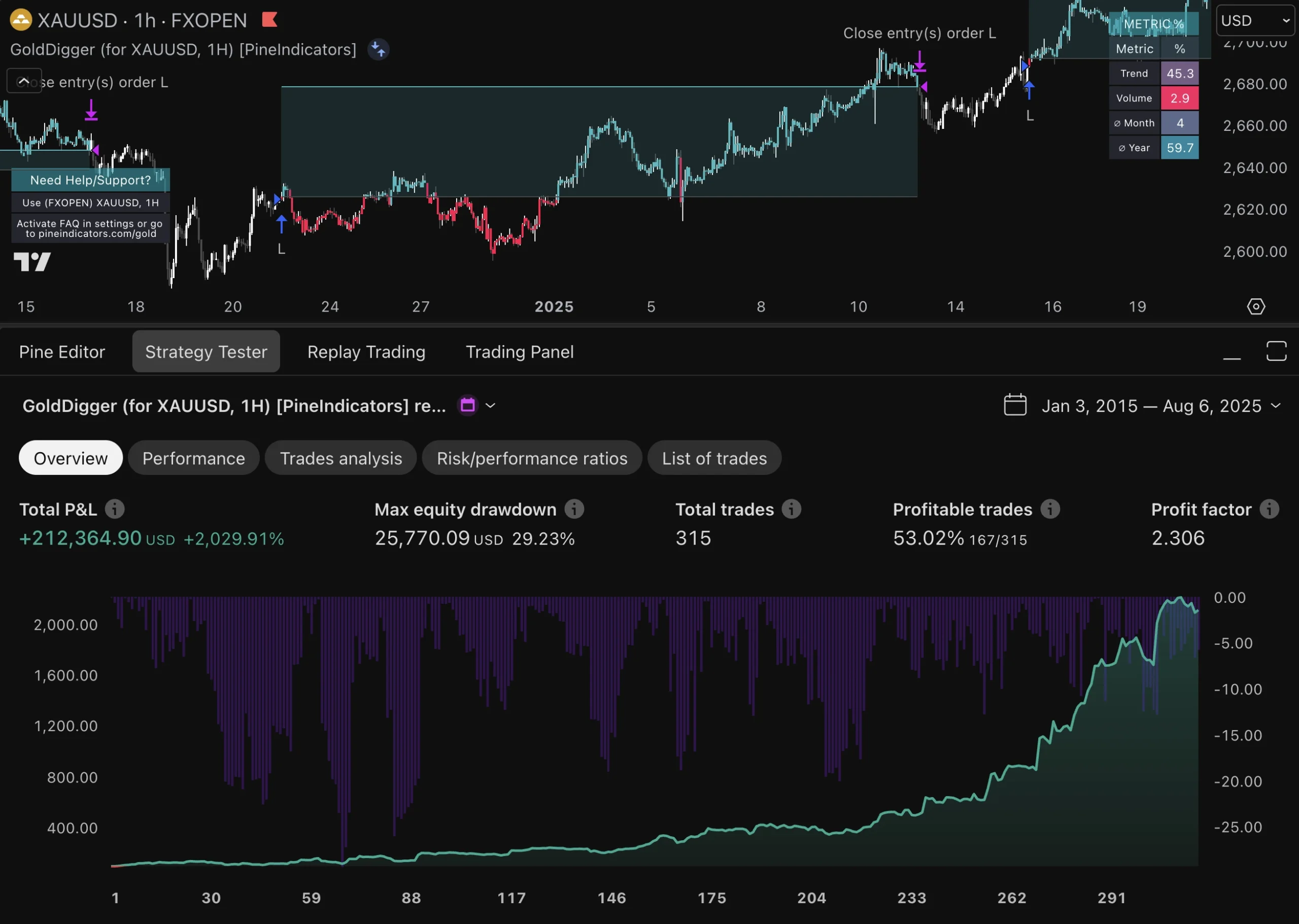
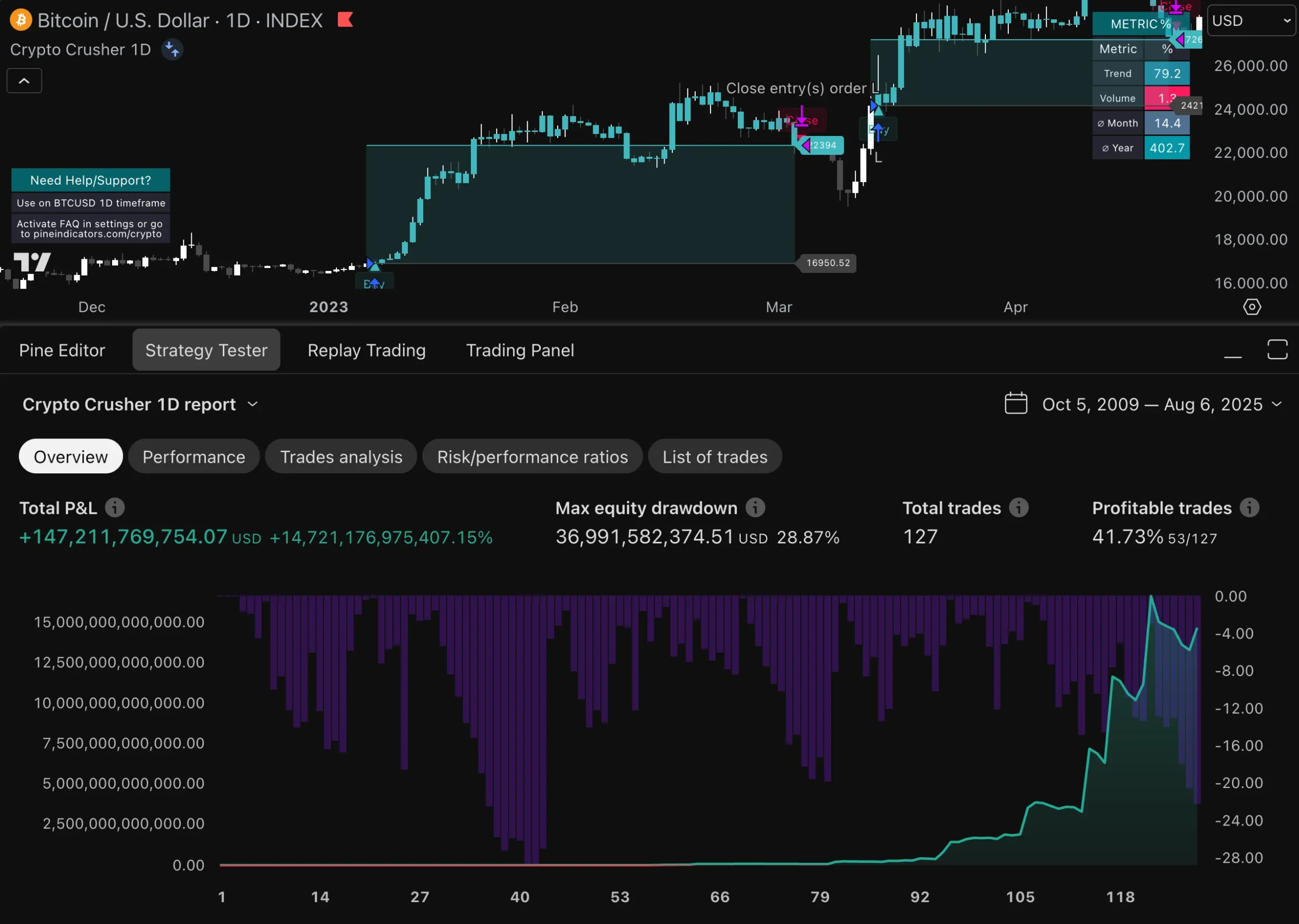
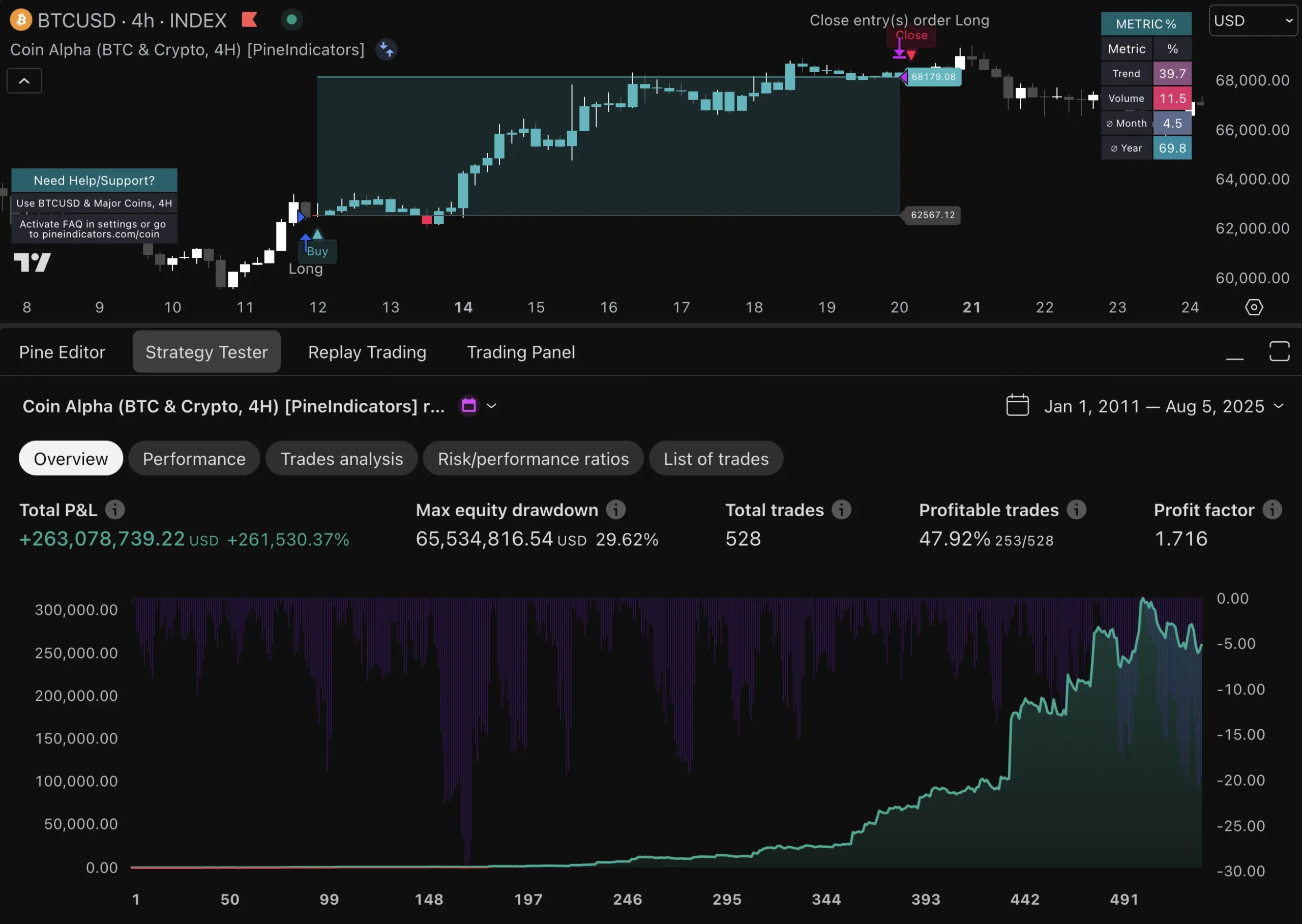
This may involve tweaking parameters or even overhauling entire strategies if they are no longer performing as expected. Moreover, traders should utilize performance metrics to evaluate their automated trades effectively. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as win rate, average profit per trade, maximum drawdown, and return on investment (ROI) provide valuable insights into how well a strategy is functioning.
By analyzing these metrics over time, traders can identify patterns or anomalies that may warrant further investigation or adjustment. For example, if a strategy consistently underperforms during specific market conditions—such as high volatility—traders may need to refine their approach or implement additional filters to enhance performance.
Evaluating the Performance of Your Automated Trading System

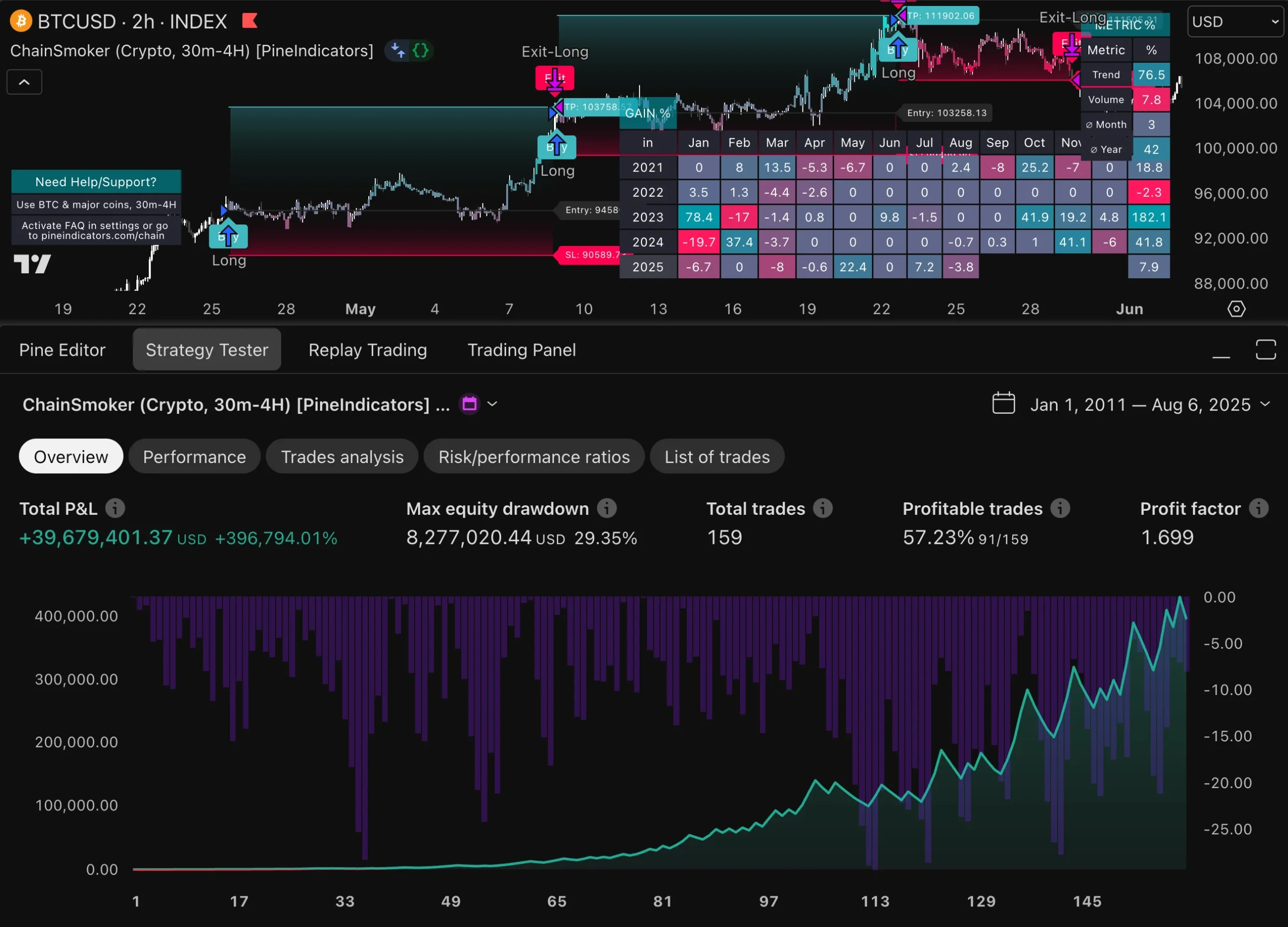
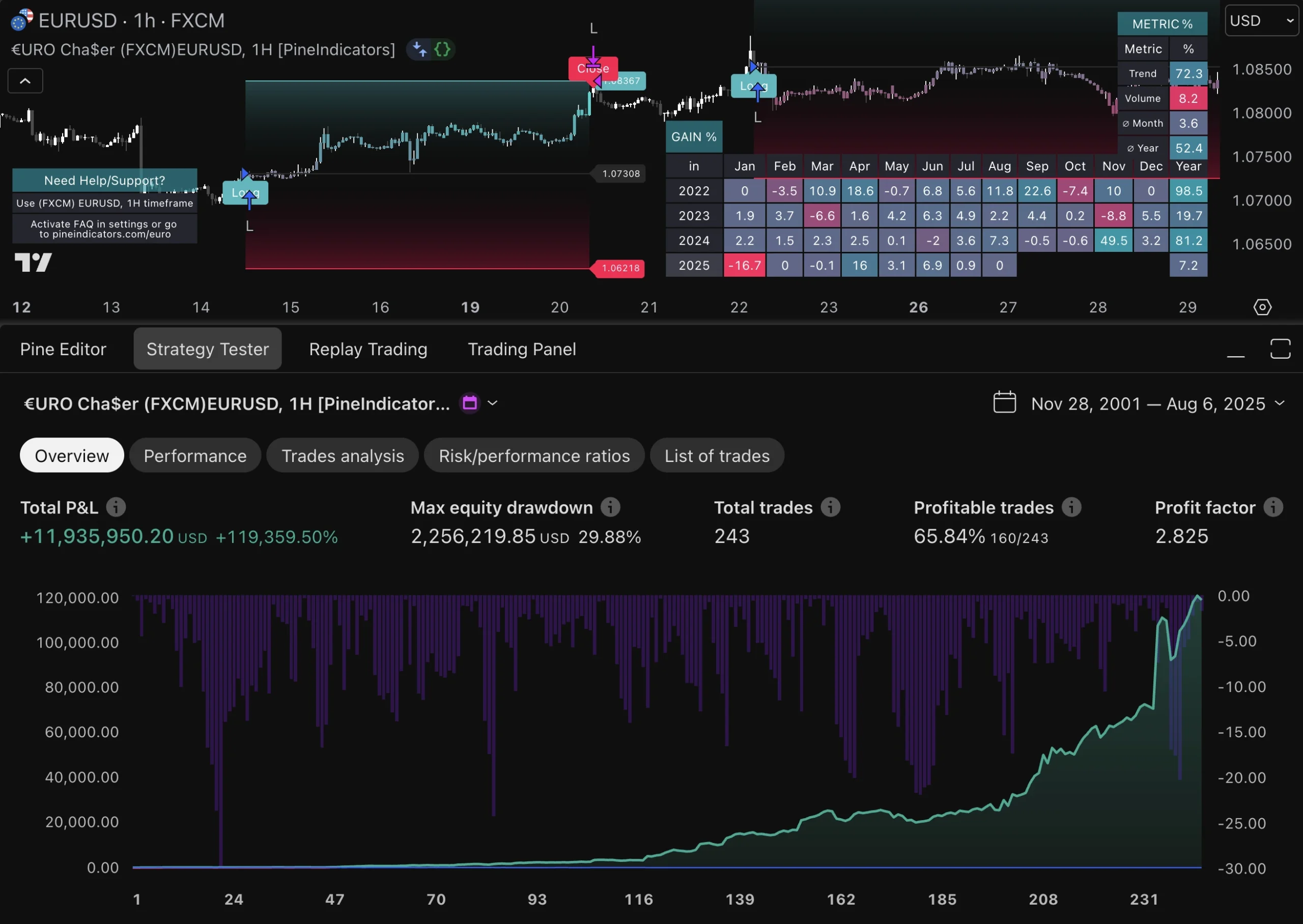
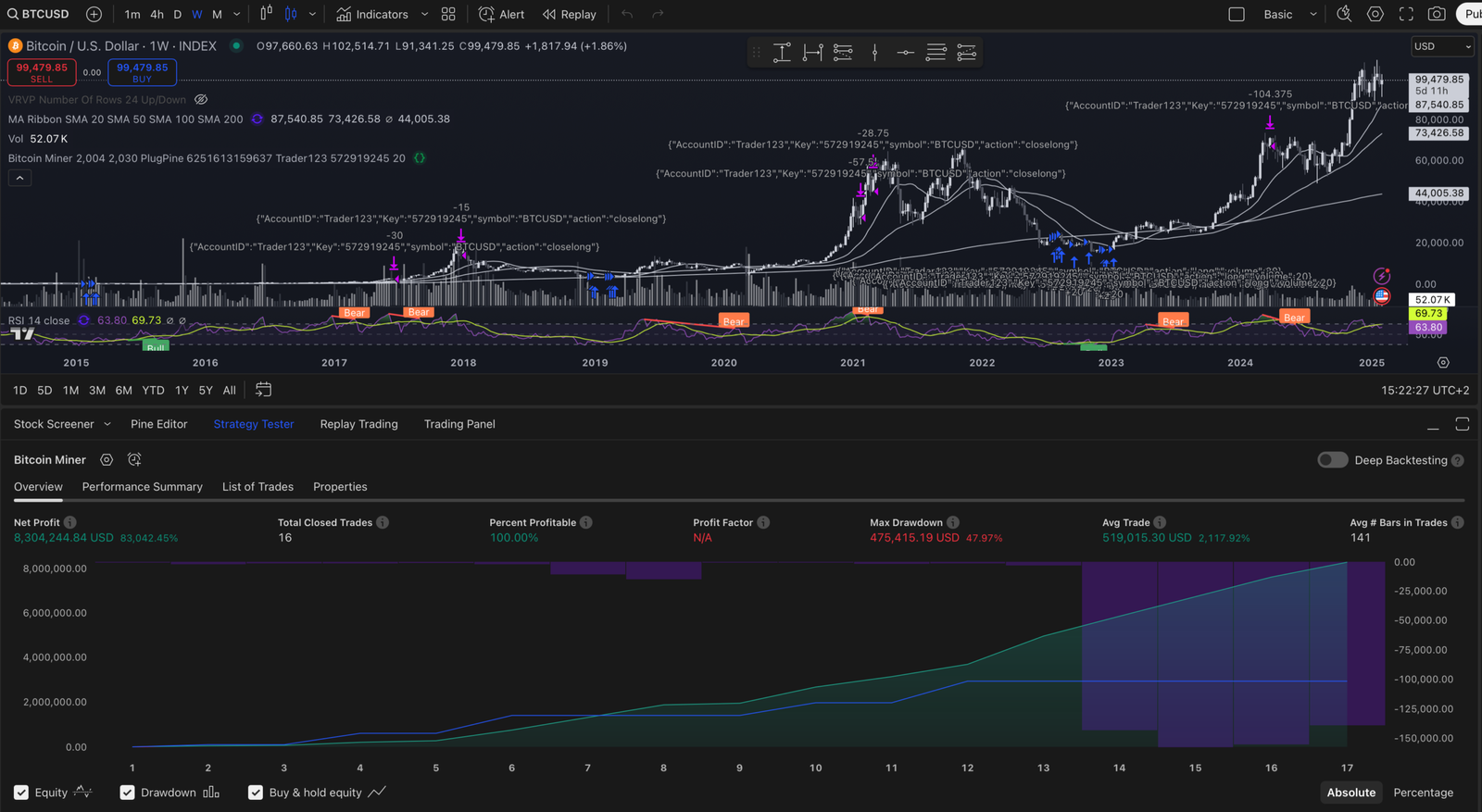
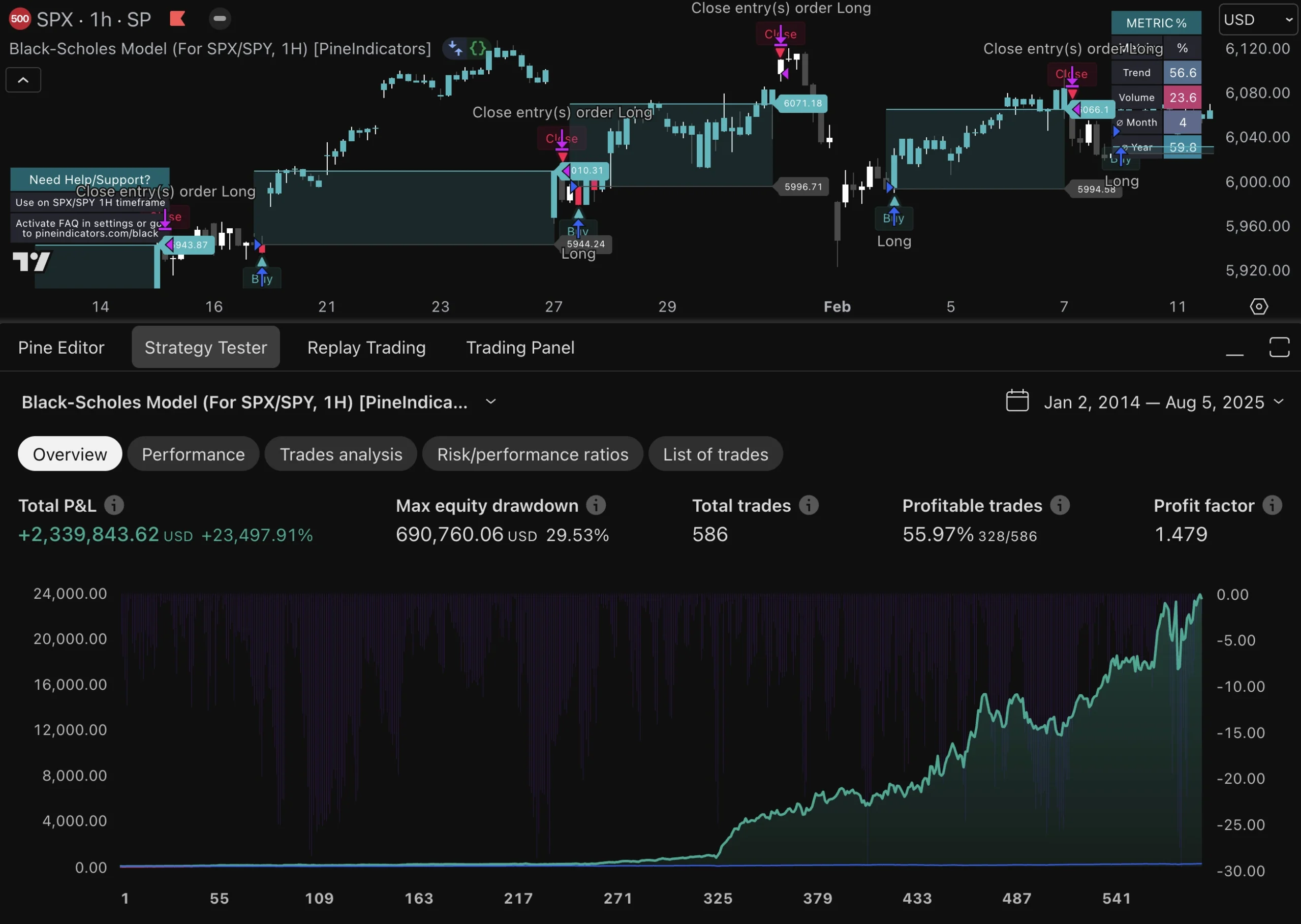
A comprehensive evaluation of an automated trading system is essential for understanding its strengths and weaknesses. This process typically involves backtesting the strategy against historical data to gauge its potential effectiveness before deploying it in live markets. Backtesting allows traders to simulate trades based on past market conditions and assess how the strategy would have performed over time.
However, it is crucial to ensure that the data used for backtesting is accurate and representative of real market conditions. In addition to backtesting, forward testing is another critical step in evaluating an automated trading system’s performance. This involves running the strategy in a live environment with real capital but often on a smaller scale or in a demo account first.
Forward testing provides insights into how the system performs under current market conditions and helps identify any issues that may not have been apparent during backtesting. By combining both backtesting and forward testing results, traders can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their system’s viability and make informed decisions about its future use.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Automated Trading
While automated trading offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges and potential pitfalls.
Another pitfall is neglecting proper risk management practices. Some traders may become overly reliant on their automated systems and fail to implement adequate safeguards against significant losses. It is essential to maintain a disciplined approach by regularly reviewing risk parameters and ensuring that stop-loss orders are in place.
Additionally, traders should avoid becoming complacent; just because a system has performed well in the past does not guarantee future success. Continuous learning and adaptation are vital components of successful automated trading.
Incorporating Fundamental Analysis into Automated Trading
While automated trading often emphasizes technical analysis through indicators and patterns, incorporating fundamental analysis can enhance decision-making processes significantly. Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic indicators, company earnings reports, geopolitical events, and other macroeconomic factors that can influence asset prices. By integrating fundamental data into automated trading systems, traders can create more robust strategies that account for broader market influences.
For instance, an automated trading algorithm could be programmed to react to economic news releases such as employment reports or interest rate changes by adjusting its trading parameters accordingly. If a positive jobs report is released, indicating economic strength, the algorithm might increase its exposure to equities while reducing positions in safe-haven assets like gold or bonds. This dynamic approach allows traders to capitalize on fundamental shifts while still relying on technical signals for entry and exit points.
Leveraging Technical Indicators in Automated Trading
Technical indicators play a pivotal role in automated trading strategies by providing quantifiable data points that inform decision-making processes. There are numerous technical indicators available—each serving different purposes—ranging from trend-following indicators like moving averages to momentum indicators such as the RSI or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence). The choice of indicators depends largely on the trader’s objectives and market conditions.
For example, a trader focused on identifying potential reversal points might utilize oscillators like the Stochastic Oscillator alongside support and resistance levels to pinpoint entry opportunities effectively. Conversely, trend-following traders may rely heavily on moving averages or Bollinger Bands to capture sustained price movements over time. By combining multiple indicators within an automated system—while ensuring they complement rather than contradict each other—traders can enhance their chances of success in various market environments.
Implementing Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders in Automated Trading
The implementation of stop-loss and take-profit orders is crucial for managing risk effectively within an automated trading framework. A stop-loss order automatically closes a position when it reaches a predetermined loss level, helping traders limit potential losses without needing constant monitoring of their trades. Similarly, take-profit orders allow traders to lock in profits by closing positions once they reach specific profit targets.
When setting these orders within an automated system, it is essential to consider market volatility and price action dynamics. For instance, placing stop-loss orders too close to entry points may result in premature exits due to normal market fluctuations. Conversely, setting them too far away could expose traders to excessive losses if adverse price movements occur.
A balanced approach involves analyzing historical volatility levels and adjusting stop-loss distances accordingly while ensuring take-profit targets align with realistic price movement expectations.
The Future of Automated Trading: AI and Machine Learning
The future of automated trading is increasingly intertwined with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize how traders develop strategies by enabling systems to learn from vast amounts of data and adapt dynamically to changing market conditions. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical price patterns alongside fundamental data inputs—identifying correlations that human traders might overlook.
For example, AI-driven systems can continuously refine their trading strategies based on real-time performance feedback—adjusting parameters automatically as new data becomes available. This level of adaptability allows for more responsive trading approaches that can capitalize on emerging trends or shifts in market sentiment more effectively than traditional methods alone. As technology continues to evolve, traders who embrace AI and machine learning will likely gain a competitive edge in navigating increasingly complex financial markets.
In conclusion, automated trading represents a powerful tool for modern traders seeking efficiency and precision in their strategies. By understanding its mechanics, choosing appropriate platforms, managing risks effectively, and leveraging both technical and fundamental analysis techniques—traders can harness the full potential of automation while remaining vigilant against common pitfalls inherent in this dynamic field.
If you’re interested in learning how to automate your trading strategies, a great resource to explore is the article on creating custom trading bots using Pine Script. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to develop and implement your own automated trading systems on TradingView, leveraging the power of Pine Script to execute trades based on your predefined criteria. For more detailed insights and step-by-step instructions, you can read the full article by visiting this link.
FAQs
What is auto trading?
Auto trading refers to the use of computer programs and software to automatically execute trading decisions in the financial markets. This can include buying and selling stocks, currencies, or other financial instruments based on pre-set criteria and algorithms.
How does auto trading work?
Auto trading works by using computer programs or algorithms to analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades without the need for human intervention. These programs can be set to follow specific trading strategies, risk management rules, and other parameters.
What are the benefits of auto trading?
Some of the benefits of auto trading include the ability to execute trades without emotions or human error, the potential for faster trade execution, the ability to backtest and optimize trading strategies, and the ability to trade across multiple markets and timeframes simultaneously.
What are the risks of auto trading?
Risks of auto trading include the potential for technical failures or glitches, the need for continuous monitoring and maintenance of the trading system, the risk of over-optimization of trading strategies, and the potential for losses due to market volatility or unexpected events.
What are some popular auto trading platforms?
Some popular auto trading platforms include MetaTrader, NinjaTrader, TradeStation, and Interactive Brokers. These platforms offer a range of features for auto trading, including the ability to develop and test trading strategies, access to historical market data, and connectivity to various brokers and markets.