High Frequency Trading (HFT) is a computerized trading method that uses algorithms and high-speed data connections to execute large volumes of trades in milliseconds. HFT systems employ quantitative models and automated processes to identify and exploit small price differences that exist for brief periods, typically lasting fractions of a second. HFT firms generate profits through high trade volumes rather than large margins per transaction, often completing thousands to millions of trades daily.
The infrastructure supporting HFT includes specialized computers with minimal processing delays, ultra-fast network connections, and sophisticated algorithms that process market data instantaneously. HFT has significantly altered financial market operations since its widespread adoption. Proponents argue that HFT increases market efficiency by narrowing bid-ask spreads and providing continuous liquidity.
Critics point to potential risks including market instability and unfair advantages over traditional investors. The rapid execution speeds characteristic of HFT can amplify market volatility, as demonstrated by events like the 2010 Flash Crash when automated trading contributed to a temporary market collapse. Research indicates that while HFT generally improves price discovery and reduces transaction costs, it can also create systemic risks during periods of market stress.
Regulatory bodies worldwide continue to evaluate HFT’s impact on market integrity. Current oversight measures include circuit breakers to halt trading during extreme volatility, minimum order resting times, and enhanced monitoring systems. The ongoing evolution of HFT technology and its market effects remain subjects of academic research and policy debate among financial regulators, market participants, and economists.
Key Takeaways
- High frequency trading involves rapid, automated transactions that require robust technology and infrastructure.
- Key risks include market liquidity issues, execution delays, and regulatory compliance challenges.
- Effective risk management involves continuous performance monitoring and strong operational controls.
- Evaluating risk-adjusted returns is essential to balance profitability against potential losses.
- Best practices focus on mitigating risks through advanced technology, regulatory adherence, and comprehensive reporting.
Identifying Performance Risks in High Frequency Strategies
Performance risks in high-frequency trading strategies can be multifaceted, stemming from various sources including market conditions, algorithmic inefficiencies, and execution challenges. One primary risk is the reliance on historical data to inform trading decisions. Algorithms are often trained on past market behavior, which may not accurately predict future movements, especially in volatile or unprecedented market conditions.
This reliance can lead to significant losses if the market behaves differently than anticipated, as the algorithms may fail to adapt quickly enough to changing circumstances. Another critical performance risk arises from the competitive nature of HFT. As more firms enter the space, the strategies that once yielded profitable returns may become less effective due to increased competition and market saturation.
This phenomenon can lead to diminishing returns on investment as traders compete for the same price discrepancies. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancement means that firms must continuously innovate their algorithms and infrastructure to maintain a competitive edge, which can be resource-intensive and fraught with risk.
Market Liquidity and Execution Risks

Market liquidity is a cornerstone of high-frequency trading, as it enables traders to enter and exit positions swiftly without significantly impacting prices. However, liquidity can be ephemeral, particularly during times of market stress or volatility. HFT strategies often rely on the assumption that there will always be sufficient liquidity to execute trades at desired prices.
When liquidity dries up, as seen during financial crises or sudden market downturns, HFT firms may find themselves unable to execute trades effectively, leading to slippage and increased transaction costs. Execution risks are closely tied to liquidity concerns. In high-frequency trading, the speed of execution is paramount; even a millisecond delay can result in missed opportunities or losses.
Factors such as network latency, server downtimes, or technical glitches can impede execution speed, undermining the effectiveness of HFT strategies. Moreover, the reliance on automated systems means that any failure in technology can lead to catastrophic outcomes, including unintended large-scale trades that can disrupt markets.
Technology and Infrastructure Risks
The technological backbone of high-frequency trading is both a strength and a vulnerability. HFT firms invest heavily in cutting-edge technology to ensure their algorithms operate at optimal speeds and efficiency. However, this dependence on technology introduces several risks.
For instance, software bugs or algorithmic errors can lead to unintended trading behaviors, resulting in significant financial losses. The infamous “Knight Capital incident” in 2012 serves as a stark reminder of this risk; a software glitch led to a $440 million loss in just 45 minutes due to erroneous trades. Infrastructure risks also encompass hardware failures and network outages.
High-frequency traders require robust systems capable of processing vast amounts of data with minimal latency. Any disruption in these systems—whether due to hardware malfunctions or external cyberattacks—can severely impact trading operations. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats poses an ongoing challenge for HFT firms, necessitating continuous investment in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
| Risk Category | Metric | Description | Typical Range | Impact on Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Risk | Volatility Exposure | Measure of sensitivity to rapid price changes | 0.5 – 2.0 (Beta) | High volatility can cause unexpected losses |
| Execution Risk | Slippage | Difference between expected and actual trade price | 0.01% – 0.1% per trade | Reduces profitability of trades |
| Technology Risk | Latency (ms) | Time delay in order execution | 1 – 10 milliseconds | Delays can cause missed opportunities or losses |
| Liquidity Risk | Order Book Depth | Volume available at best bid/ask prices | 1000 – 10000 units | Low liquidity increases market impact costs |
| Operational Risk | System Downtime | Duration of system unavailability | 0 – 5 minutes per day | Interrupts trading and causes missed trades |
| Regulatory Risk | Compliance Breaches | Number of violations or warnings | 0 – 1 per year | Can lead to fines and strategy suspension |
| Model Risk | Backtest Overfitting | Degree to which model fits historical noise | Low to High (qualitative) | Leads to poor real-world performance |
The regulatory landscape surrounding high-frequency trading is complex and continually evolving. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing HFT practices due to concerns about market manipulation, systemic risk, and fairness. Compliance with regulations such as the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) in Europe or the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States requires firms to implement stringent reporting and transparency measures.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and reputational damage. Moreover, regulatory changes can introduce uncertainty into HFT strategies. For instance, new rules regarding order types or market access can alter the competitive dynamics of trading strategies overnight.
Firms must remain agile and adaptable to navigate these changes effectively while ensuring compliance with existing regulations. This necessitates ongoing investment in compliance infrastructure and legal expertise, further complicating the operational landscape for high-frequency traders.
Operational and Counterparty Risks

Operational risks in high-frequency trading encompass a wide range of potential issues that can disrupt trading activities. These include human errors in algorithm development or execution, inadequate risk management practices, and failures in internal processes or controls. Given the automated nature of HFT, even minor operational missteps can lead to significant financial repercussions.
For example, if an algorithm is incorrectly calibrated or fails to account for certain market conditions, it may execute trades that result in substantial losses. Counterparty risks are another critical consideration for HFT firms. These risks arise from the possibility that a counterparty may default on their obligations during a trade execution or settlement process.
In high-frequency trading environments where transactions occur at lightning speed, the failure of a counterparty to fulfill their end of a trade can lead to immediate financial losses and disrupt trading strategies. To mitigate these risks, firms often engage in thorough due diligence when selecting counterparties and may employ collateral agreements or other risk-sharing mechanisms.
Risk Management and Control Measures
Effective risk management is essential for high-frequency trading firms seeking to navigate the myriad performance risks associated with their strategies. A comprehensive risk management framework should encompass both quantitative and qualitative measures tailored to the specific characteristics of HFT operations.
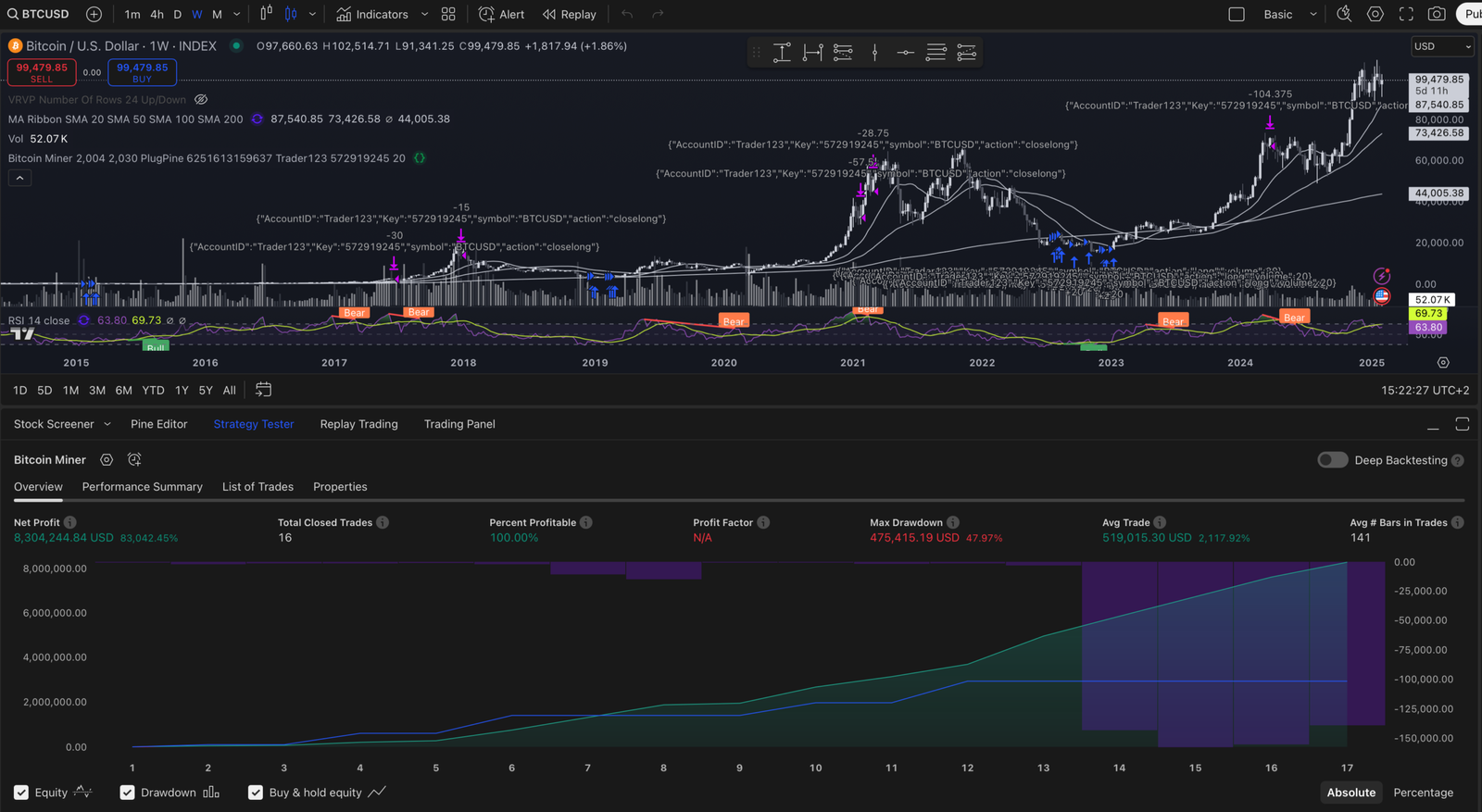
Additionally, firms should employ stress testing and scenario analysis to evaluate how their strategies would perform under various market conditions. By simulating extreme market events or adverse scenarios, traders can identify potential vulnerabilities within their algorithms and make necessary adjustments before real-world implementation. Furthermore, continuous backtesting against historical data allows firms to refine their models and enhance their predictive accuracy over time.
Performance Monitoring and Reporting
Performance monitoring is a critical component of managing high-frequency trading strategies effectively. Given the rapid pace at which trades are executed, real-time performance tracking is essential for identifying trends and anomalies that may indicate underlying issues with trading algorithms or market conditions. Advanced analytics tools can provide insights into key performance indicators (KPIs), such as execution speed, slippage rates, and profitability metrics.
Regular reporting is also vital for maintaining transparency with stakeholders and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Firms should establish standardized reporting protocols that detail performance outcomes, risk exposures, and compliance metrics. This not only aids in internal decision-making but also fosters trust among investors and regulators by demonstrating a commitment to accountability and responsible trading practices.
Evaluating Risk-Adjusted Returns
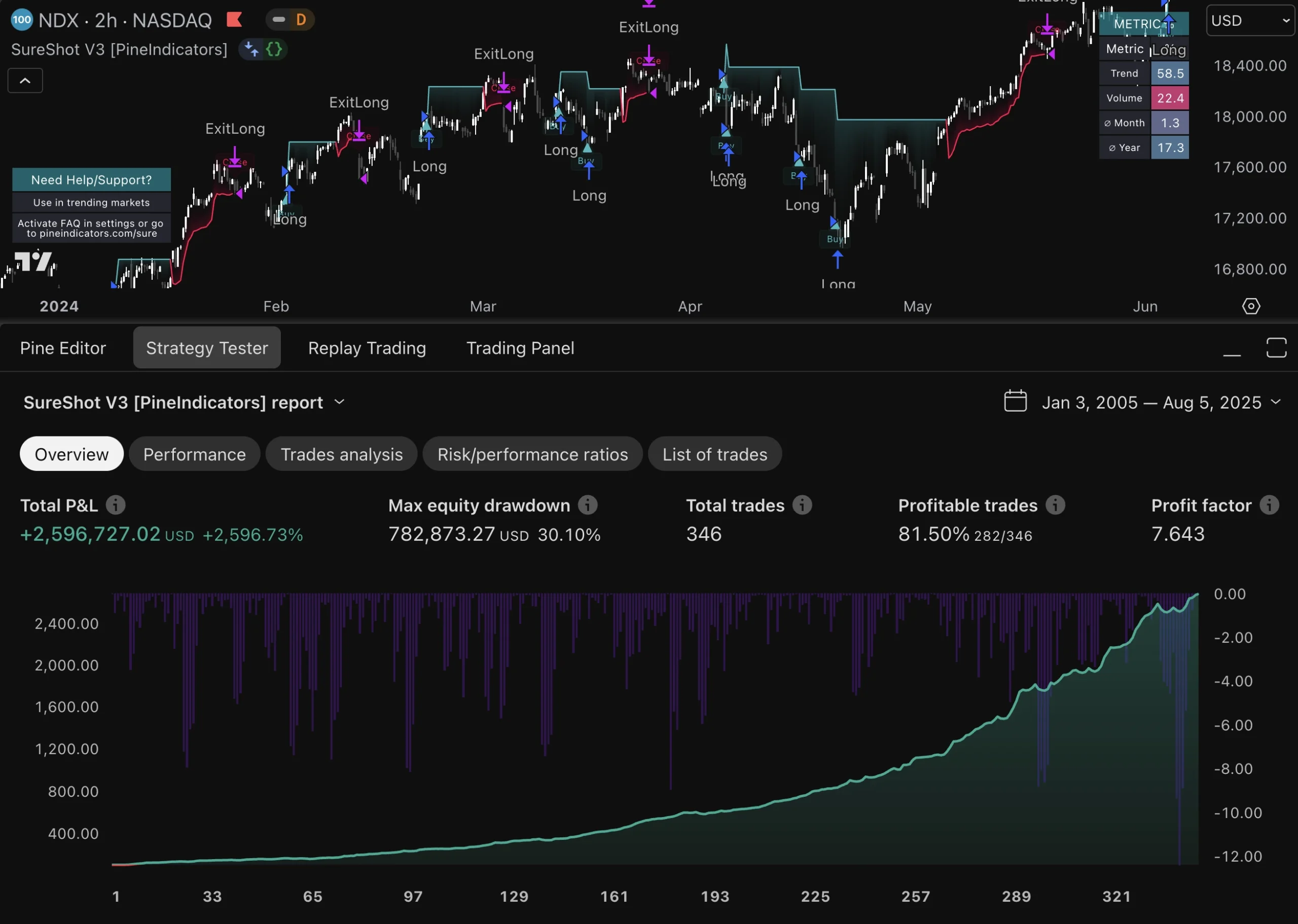
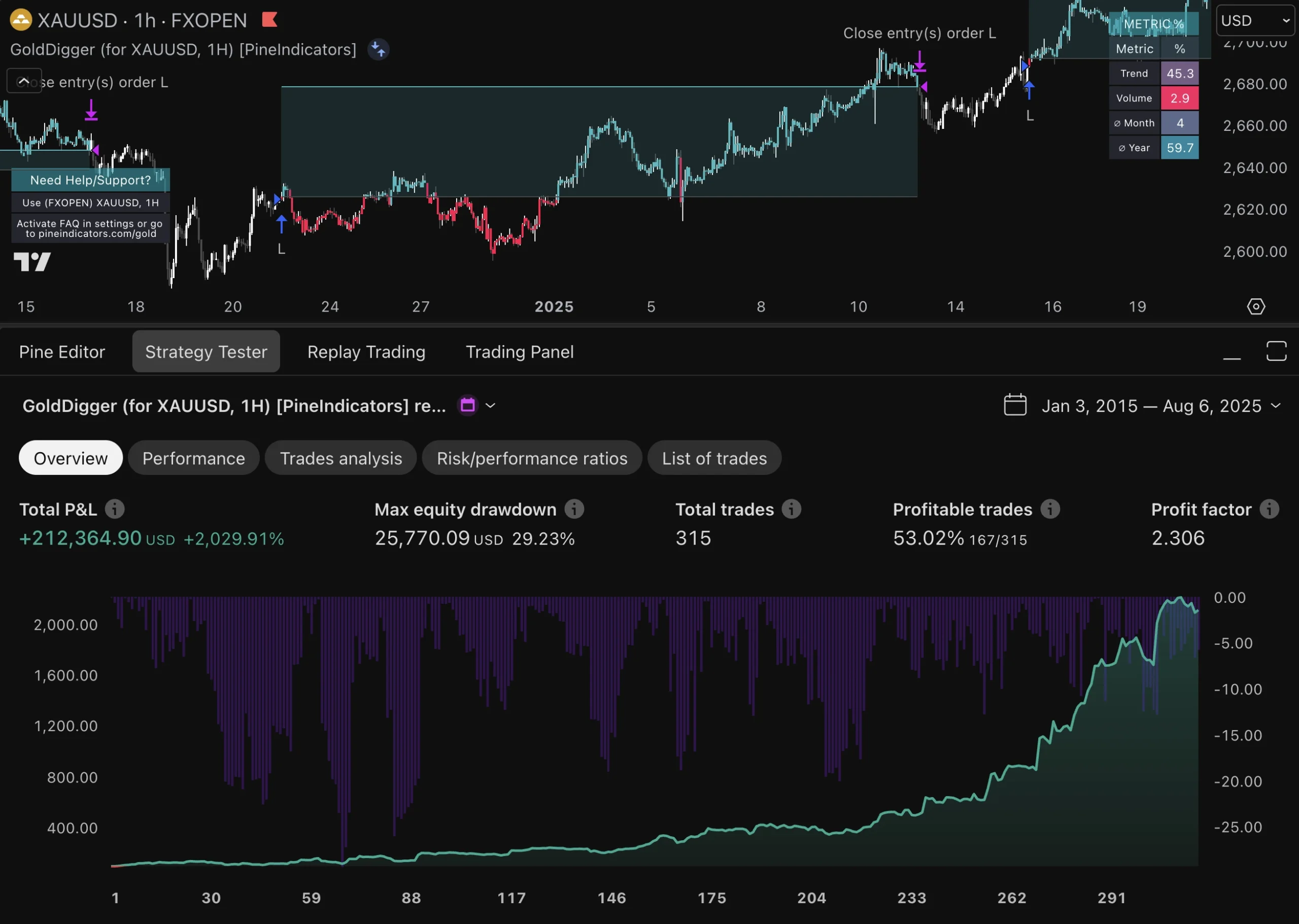
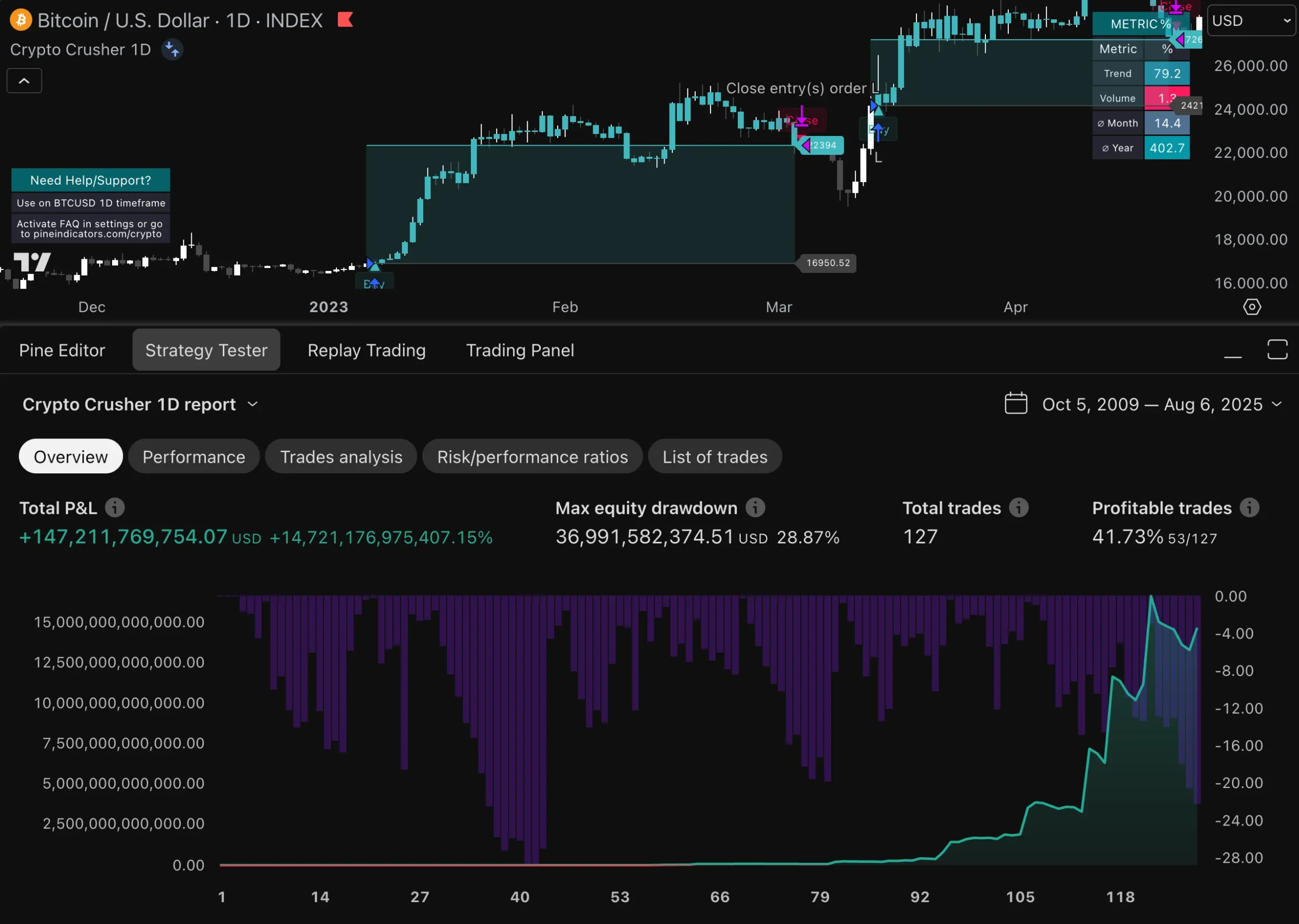
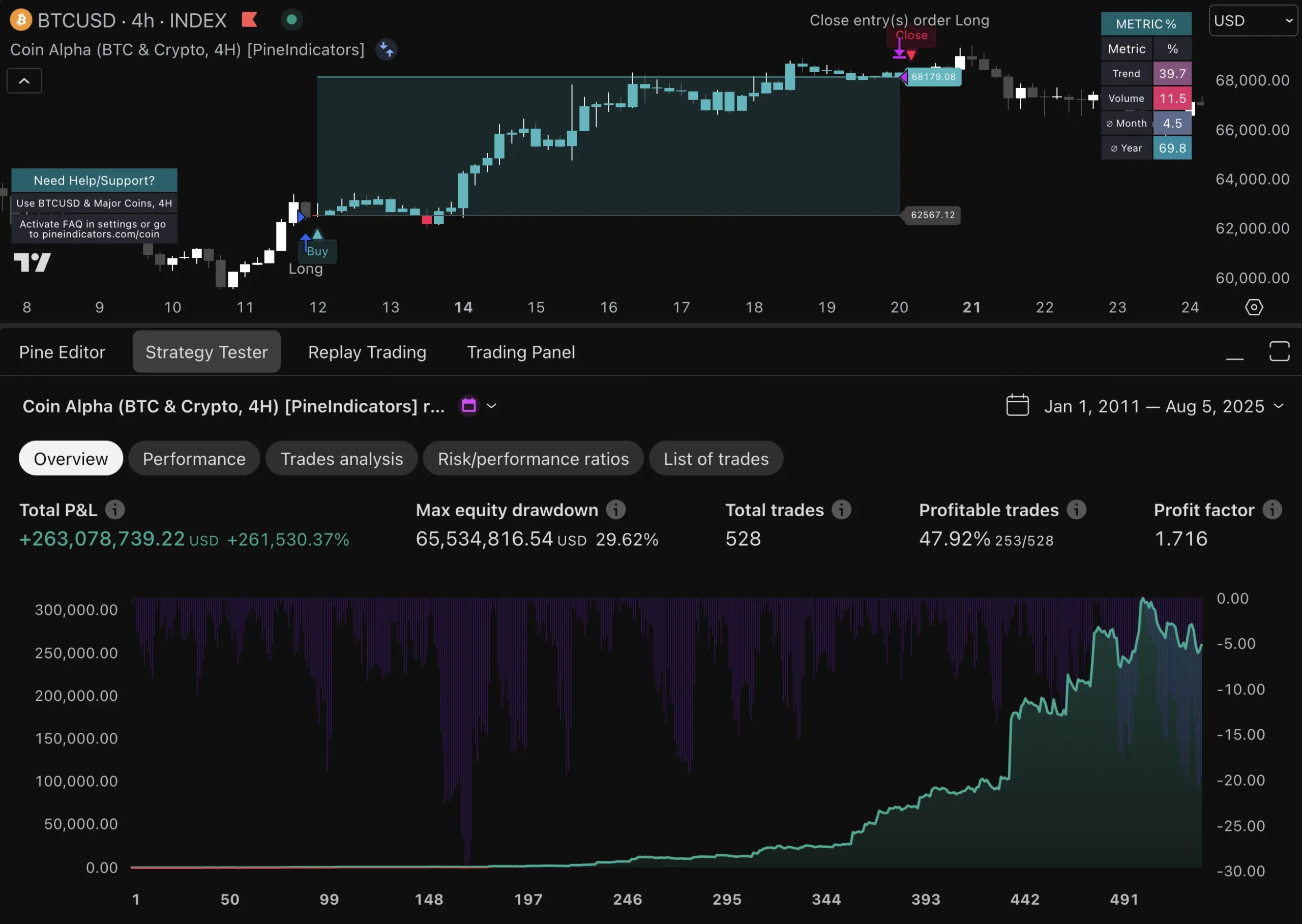
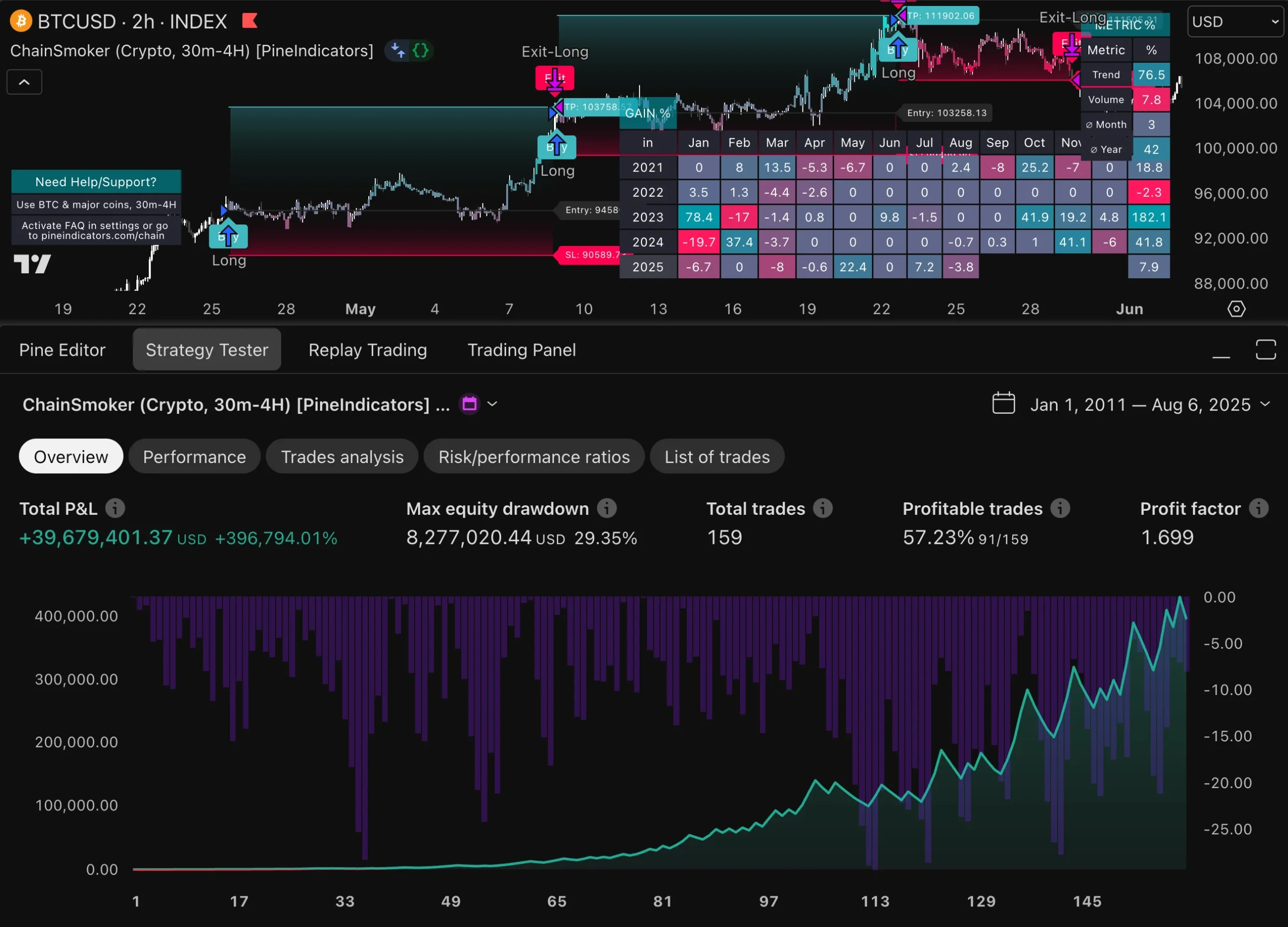
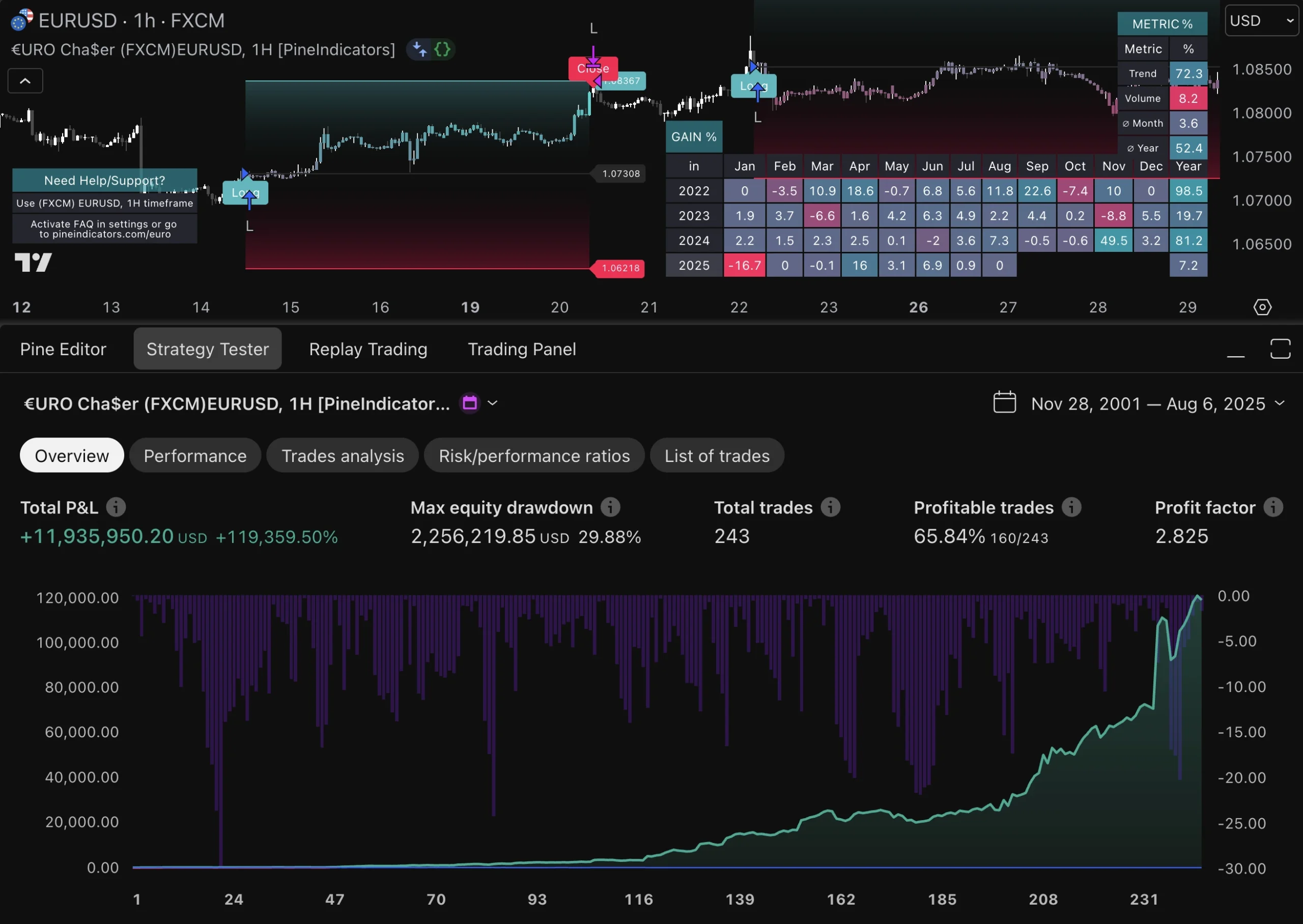
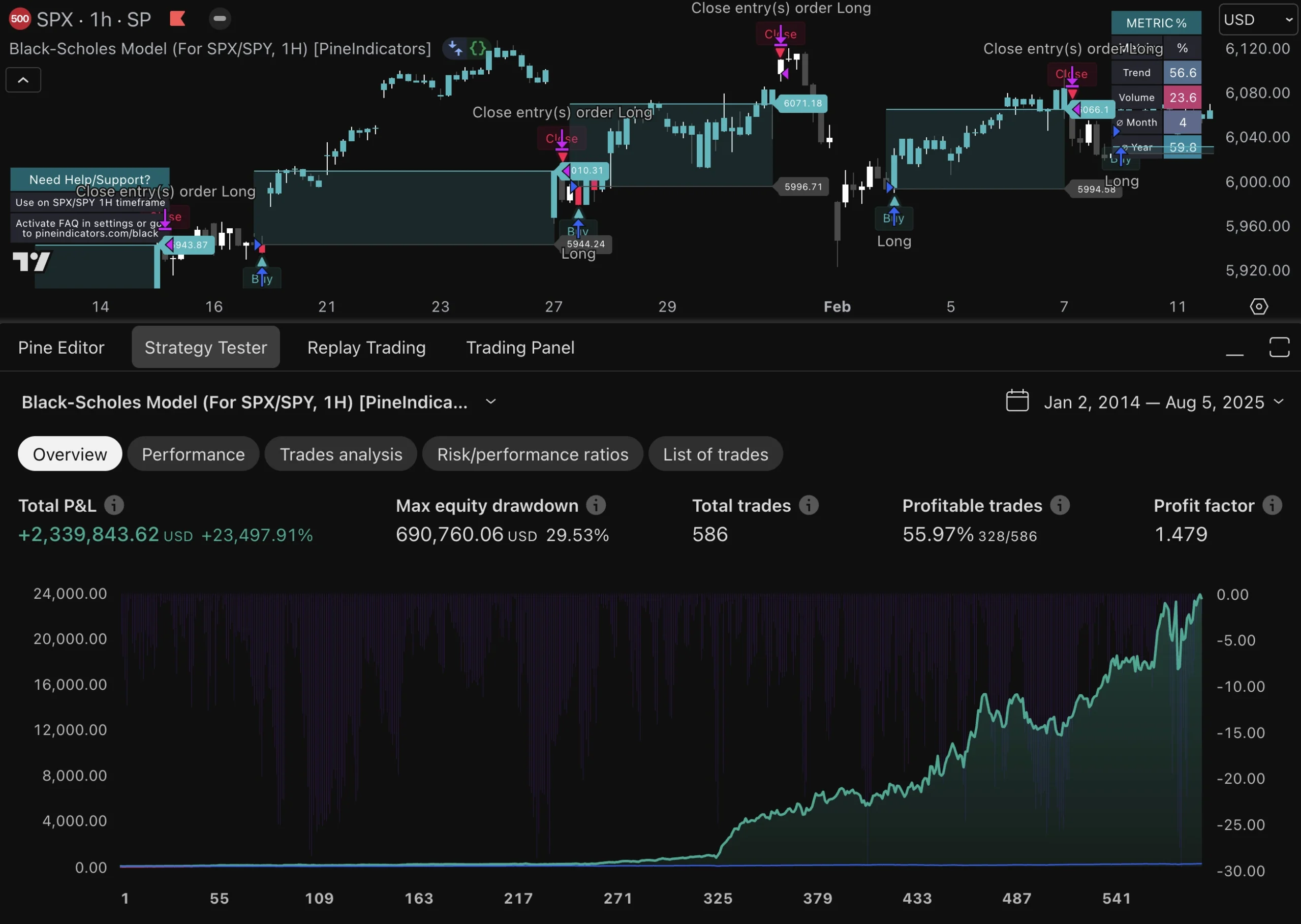
In high-frequency trading, evaluating risk-adjusted returns is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of trading strategies relative to their inherent risks. Traditional performance metrics such as return on investment (ROI) may not adequately capture the complexities associated with HFT due to its unique risk profile. Instead, metrics like the Sharpe ratio or Sortino ratio provide more nuanced insights by factoring in volatility and downside risk.
By focusing on risk-adjusted returns, traders can better understand how well their strategies perform relative to the risks taken. This evaluation process enables firms to identify underperforming strategies that may require reevaluation or adjustment while highlighting successful approaches that warrant further investment or scaling.
Mitigating Performance Risks in High Frequency Strategies
Mitigating performance risks in high-frequency trading requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technology enhancements, robust risk management practices, and continuous adaptation to changing market conditions. One effective strategy is diversifying trading algorithms across different asset classes or markets to reduce exposure to specific risks associated with any single strategy or market environment. Additionally, implementing fail-safes within trading algorithms can help prevent catastrophic losses during periods of extreme volatility or unexpected market events.
For instance, incorporating circuit breakers that halt trading when certain thresholds are met can provide valuable time for traders to reassess their positions before executing further trades. Continuous education and training for personnel involved in algorithm development and execution are also vital for mitigating performance risks. By fostering a culture of learning and adaptability within HFT firms, organizations can better equip their teams to respond effectively to emerging challenges while enhancing overall operational resilience.
Best Practices for Navigating High Frequency Strategy Performance Risks
Navigating performance risks in high-frequency trading requires a proactive approach grounded in best practices across various domains including technology management, regulatory compliance, and operational resilience. Firms must prioritize investment in advanced technology while ensuring robust risk management frameworks are in place to address potential vulnerabilities inherent in their strategies. Moreover, fostering a culture of transparency through regular performance monitoring and reporting enhances accountability while building trust among stakeholders.
By focusing on risk-adjusted returns and continuously refining their strategies based on empirical data and market feedback, high-frequency traders can position themselves for sustained success amidst an ever-evolving landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements and regulatory scrutiny.
High-frequency trading strategies can offer significant opportunities for profit, but they also come with a unique set of performance risks that traders must navigate. For a deeper understanding of how to effectively test and optimize trading strategies, you can refer to the article on the TradingView strategy tester, which provides valuable insights into evaluating strategy performance. Check it out here: com/tradingview-strategy-tester/’>TradingView Strategy Tester.
FAQs
What is high frequency trading (HFT)?
High frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading that uses powerful computers and sophisticated algorithms to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds, often in fractions of a second.
What are the common performance risks associated with high frequency trading strategies?
Common performance risks include technological failures, latency issues, market volatility, regulatory changes, and the risk of algorithmic errors that can lead to significant financial losses.
How does latency affect high frequency trading performance?
Latency, or the delay between order submission and execution, can negatively impact HFT performance by causing missed trading opportunities or unfavorable trade prices, reducing overall profitability.
What role does market volatility play in high frequency strategy risks?
Market volatility can increase the risk of rapid price changes, which may lead to unexpected losses or the triggering of stop-loss orders, making it challenging for HFT strategies to maintain consistent performance.
Can technological failures impact high frequency trading strategies?
Yes, technological failures such as hardware malfunctions, software bugs, or connectivity issues can disrupt trading operations, leading to missed trades or erroneous orders that affect performance.
Are regulatory changes a risk factor for high frequency trading?
Yes, changes in financial regulations can impose new restrictions or requirements on HFT activities, potentially increasing compliance costs or limiting trading strategies, thereby affecting performance.
How can algorithmic errors affect high frequency trading?
Algorithmic errors can cause incorrect trade executions, unintended market positions, or excessive risk exposure, which may result in significant financial losses and damage to a trading firm’s reputation.
What measures can be taken to mitigate performance risks in high frequency trading?
Mitigation measures include rigorous testing and validation of algorithms, robust risk management protocols, real-time monitoring systems, infrastructure redundancy, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Is high frequency trading suitable for all investors?
No, high frequency trading requires significant technological resources, expertise, and risk tolerance, making it more suitable for institutional investors and specialized trading firms rather than individual investors.
How does competition affect high frequency trading performance?
High competition in HFT can lead to diminishing returns as many firms use similar strategies, making it essential to continuously innovate and optimize algorithms to maintain a competitive edge.