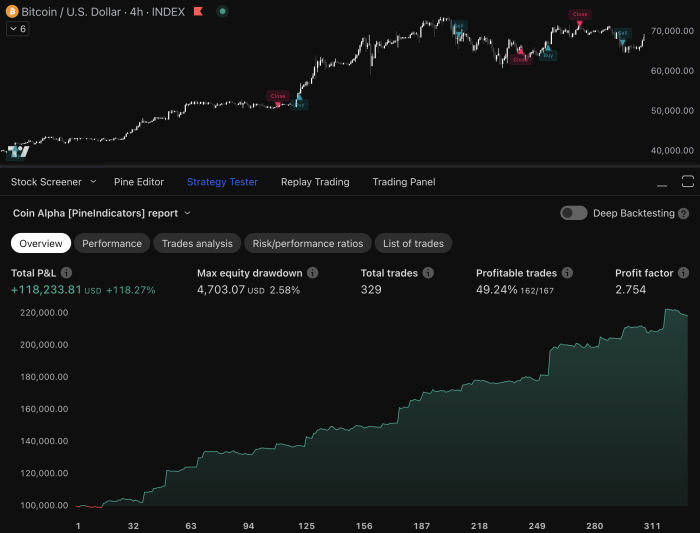
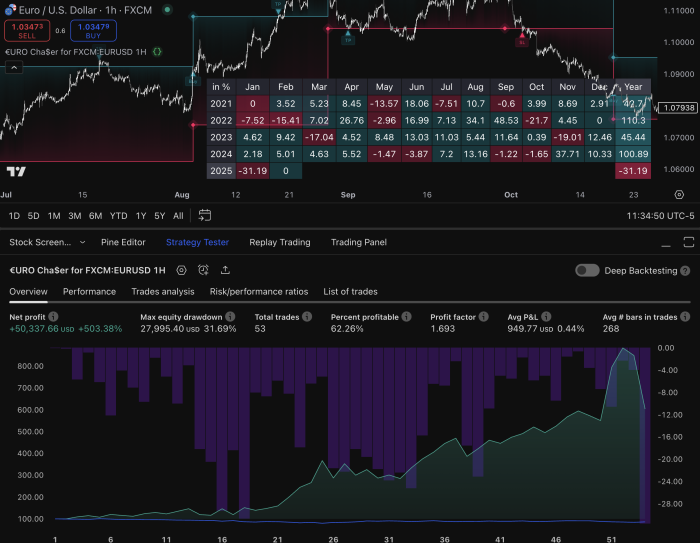
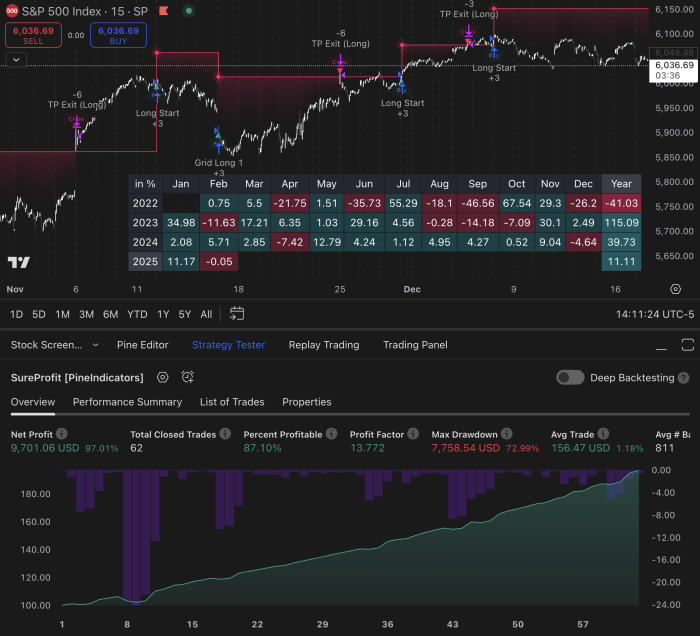
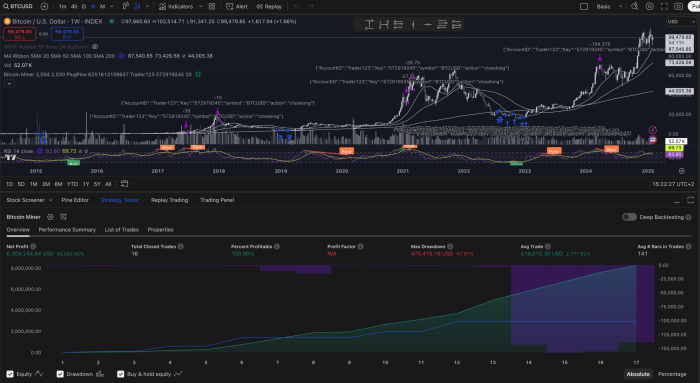
To navigate the complexities of financial markets, one must first grasp the fundamental principles that govern them. The market is a dynamic ecosystem influenced by a myriad of factors, including economic indicators, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone looking to engage in trading or investing.
For instance, economic indicators such as GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, and inflation data can significantly impact market movements. A robust economy typically leads to increased consumer spending, which can drive stock prices higher. Conversely, negative economic news can trigger sell-offs, highlighting the importance of staying informed about macroeconomic trends.
Moreover, the market is not just a collection of numbers; it is a reflection of human behavior and psychology. Investor sentiment can sway markets dramatically, often leading to irrational exuberance or panic selling. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, initial fears led to a sharp decline in stock prices, but as governments implemented stimulus measures and vaccine developments progressed, markets rebounded with unprecedented speed.
Understanding these psychological factors can provide traders with insights into potential market movements and help them make more informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the market is crucial for successful trading
- Setting realistic goals helps in managing expectations and staying focused
- Risk management is essential to protect your capital and minimize losses
- Utilizing technical analysis can help in identifying trends and making informed decisions
- Implementing fundamental analysis is important for understanding the underlying value of assets
- Developing a trading plan provides a structured approach to trading
- Diversifying your portfolio helps in spreading risk and maximizing potential returns
- Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead in the ever-changing market landscape
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting SMART Goals
Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, rather than setting a vague goal of “making money,” a trader might aim to achieve a 10% return on investment within six months by employing a specific trading strategy. This clarity not only provides direction but also helps in evaluating performance over time.
Aligning Goals with Risk Tolerance and Investment Horizon
Additionally, it is essential to align trading goals with one’s risk tolerance and investment horizon. A trader with a high-risk tolerance may set aggressive targets, while a more conservative investor might prioritize capital preservation over high returns.
Adjusting Goals to Market Conditions
Understanding personal financial situations and market conditions can help in setting realistic expectations. For example, during periods of high volatility, it may be prudent to adjust goals to account for increased risk rather than sticking rigidly to pre-established targets.
Risk Management

Effective risk management is paramount in trading and investing, as it helps protect capital and ensures long-term sustainability. One of the fundamental principles of risk management is the concept of position sizing, which involves determining how much capital to allocate to each trade based on the overall portfolio size and risk tolerance. For instance, a common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of the total portfolio on a single trade.
This approach allows traders to withstand a series of losses without jeopardizing their entire investment. Another critical aspect of risk management is the use of stop-loss orders. These orders automatically sell a security when it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
For example, if a trader buys shares at $50 and sets a stop-loss order at $45, they will exit the position if the price falls to that level, thereby capping their loss at 10%. This strategy not only protects capital but also helps traders maintain emotional discipline by removing the need for real-time decision-making during market fluctuations.
Utilizing Technical Analysis
| Technical Analysis Metric | Data |
|---|---|
| Simple Moving Average (SMA) | 50-day SMA: 120.56 |
| Exponential Moving Average (EMA) | 200-day EMA: 135.72 |
| Relative Strength Index (RSI) | 14-day RSI: 65.89 |
| Bollinger Bands | Upper Band: 150.20 |
| MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) | MACD Line: 5.32 |
Technical analysis is a powerful tool that traders use to evaluate securities and forecast future price movements based on historical price patterns and trading volume. By analyzing charts and various indicators, traders can identify trends and potential reversal points in the market. For instance, moving averages are commonly used to smooth out price data and identify the direction of the trend.
A trader might look for a crossover between the short-term moving average and the long-term moving average as a signal to enter or exit a position. Moreover, technical analysis encompasses various chart patterns such as head and shoulders, flags, and triangles that can indicate potential price movements. For example, a head-and-shoulders pattern often signals a reversal from bullish to bearish sentiment.
Traders who recognize these patterns can position themselves advantageously before significant price changes occur. Additionally, tools like Relative Strength Index (RSI) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can provide insights into overbought or oversold conditions, further aiding in decision-making.
Implementing Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis focuses on price movements and patterns, fundamental analysis delves into the intrinsic value of an asset by examining economic factors, financial statements, and industry conditions. This approach is particularly valuable for long-term investors who seek to understand the underlying health of a company or asset before making investment decisions. For instance, analyzing a company’s earnings reports, revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels can provide insights into its financial stability and growth potential.
Furthermore, macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation rates, and overall economic growth play a crucial role in fundamental analysis. For example, rising interest rates may negatively impact consumer spending and corporate profits, leading to lower stock prices across various sectors. Investors who stay attuned to these economic indicators can make more informed decisions about when to buy or sell assets based on their potential impact on market conditions.
Developing a Trading Plan

Defining Trading Strategies
For instance, a trader might decide to enter positions based on specific technical indicators while setting clear profit targets and stop-loss levels for each trade.
Evaluating Performance
Moreover, the trading plan should include guidelines for reviewing performance regularly. By analyzing past trades—both successful and unsuccessful—traders can identify patterns in their decision-making processes and refine their strategies accordingly.
Discipline and Refining Skills
This iterative approach not only enhances trading skills but also fosters discipline by encouraging adherence to the plan even during periods of market volatility or emotional stress.
Diversifying Your Portfolio
Diversification is a fundamental principle in investing that involves spreading capital across various assets to reduce risk exposure. By holding a mix of asset classes—such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate—investors can mitigate the impact of poor performance in any single investment on their overall portfolio. For example, during economic downturns when stock prices may decline sharply, bonds or other fixed-income securities may provide stability and income.
Additionally, diversification can be achieved through geographic allocation by investing in international markets or sectors that respond differently to economic conditions. For instance, technology stocks may perform well during periods of innovation and growth while utility stocks may offer stability during economic downturns due to their consistent demand. By carefully selecting a diverse range of investments that are not closely correlated with one another, investors can enhance their chances of achieving more stable returns over time.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The financial markets are constantly evolving due to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifts in investor behavior. As such, continuous learning is essential for traders and investors who wish to remain competitive in this dynamic environment. Engaging with educational resources such as books, online courses, webinars, and financial news can provide valuable insights into new strategies and market trends.
Moreover, adapting to changing market conditions is crucial for long-term success. Traders should be willing to reassess their strategies based on new information or shifts in market dynamics. For instance, during periods of heightened volatility or changing economic conditions, it may be necessary to adjust risk management techniques or reevaluate asset allocations within a portfolio.
By fostering a mindset of continuous improvement and flexibility, traders can better navigate the complexities of the financial markets while positioning themselves for future success.
If you are looking to enhance your trading strategy, you may want to consider using custom Pine Script indicators. These indicators can help you identify key trends and patterns in the market, giving you an edge when making trading decisions.
Pine Indicators offers a free library of indicators that you can use to improve your trading strategy.
Additionally, they also provide a custom Pine Script indicator service that allows you to create personalized indicators tailored to your specific trading needs. Check out their article on how custom Pine Script indicators can enhance your trading strategy {lazyloadBackgroundObserver.observe(lazyloadBackground)})};const events=['DOMContentLoaded','elementor/lazyload/observe',];events.forEach((event)=>{document.addEventListener(event,lazyloadRunObserver)})